Core elements of human resource management system
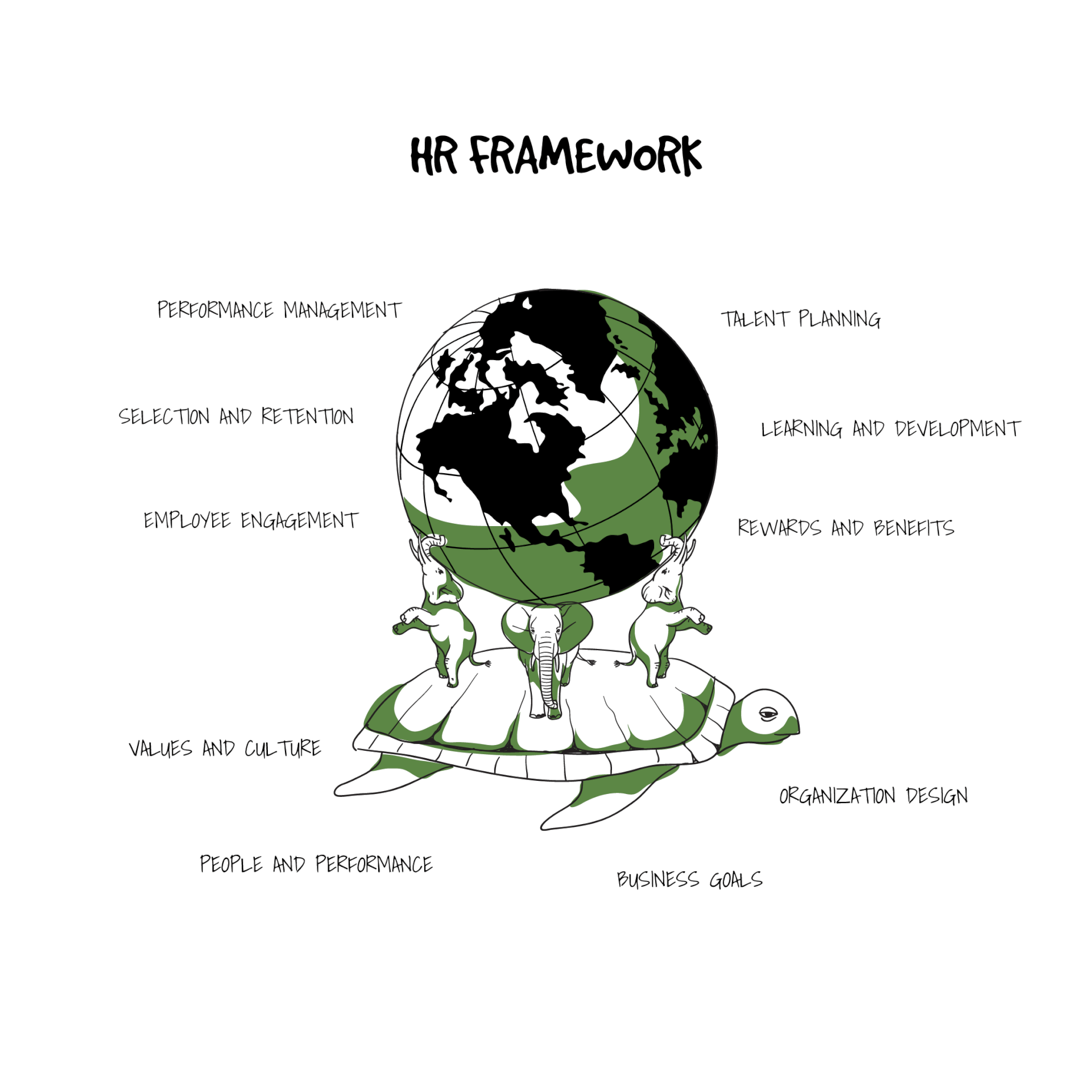
HR framework
The ultimate objective of human resource management involves integrating all programs and policies related to the business of managing employees within the framework of a firm’s strategy.
Strategic human resource management relates to the development of a consistent set of practices, policies, and codes of conduct to facilitate translating the business targets into the people management goals.
Each firm varies in its approaches and processes as well as its functional areas. Still, all HR policies and programs more or less consistent and are integrated into a broader HR framework.
Typically, the main responsibilities of the human resource department are to deal with the entry and exit process of employees, development and growth management, reward and disciplinary practices, legal compliance, and strategic initiatives.
People management is a critical feature of human resource management, involving rectifying problems between line managers and subordinates, recruitment and screening, etc.
The key guiding principles being the recognition that people are critical to a firm and investment in the right people can achieve the greatest financial return are imperative to improving the results for all stakeholders.
Any basic strategy involves an HR framework of the following pattern: recruitment, selection, onboarding, training, work environment, performance, development and reward.
Advances in technology, the changing economic conditions, workforce demographics require HR professionals to reinvent their roles. In the face of technologies like social media, companies now have to revisit their outdated strategies and frameworks for dealing with their employees.
Personnel administrators need to consider the use of technology and social media as well as reliance on data and analytics. It is important to optimize every touchpoint in the employees’ journey in the company and focus upon the needs of the employees in both the recruitment process, during their employment, and even while exiting.
For an effective HR framework, it is vital to not only focus on diagnostic metrics and KPIs but also engage the staff using employee surveys and polls. Detailed leadership feedbacks and assessment of new hires will show how healthy is the work environment at the firm. Thus, there is a need for a data and communication driven HR framework.
HR cycle
The human resources life cycle (also called the employee life cycle) refers to the various stages of an employees’ time at a particular firm and the varied roles that the human resources function plays at each of these stages.
There are many models of the HR cycle:
- The three-stage model pertains to functions like recruitment, retention, and redeployment.
- The four-stage model encompasses recruitment, training, evaluation, and promotion.
- The five-stage model includes recruitment, education, motivation, evaluation, and celebration.
- The seven-stage model incorporates recruitment, management, reward, training, motivation, policies, and evaluation.
- The eight-stage model is the most extensive including functional areas and responsibilities like job description, selection and placement, organizational design, skill assessment, training and education, performance management, rewards and compensation, and career planning and development.
These HR cycle models describe the roles played by the HR department within the employment life span of an employee from receiving applications and resumes, interviewing and selection, hiring, through stages like employment, management, development, and to exit.
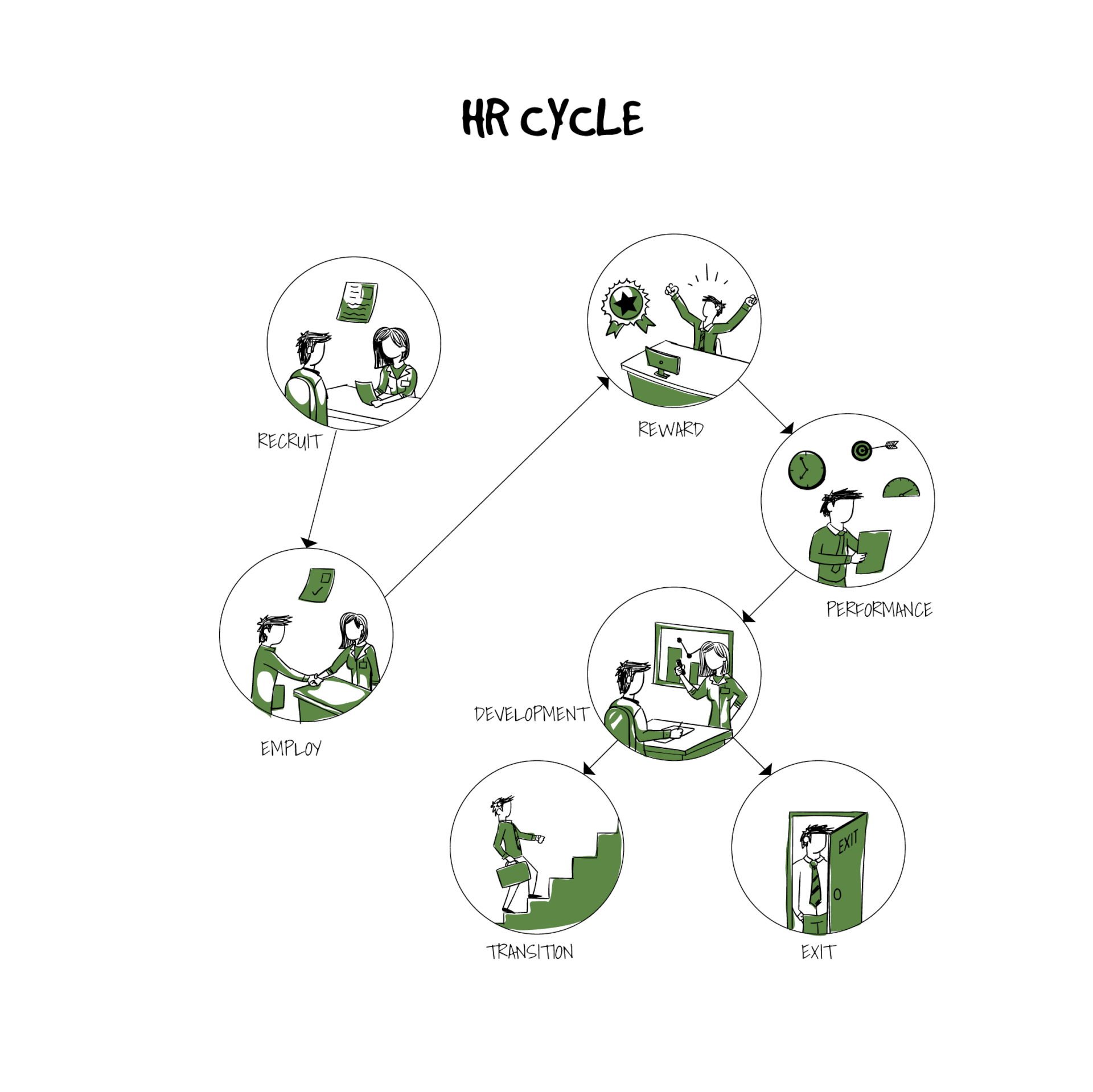
Each HR role presents its own particular challenges thus, creating a need to take measures to address the problems so that both the employees and the firm continue to grow. No doubt HR has the weight of the responsibility to recruit competent staff in a fair manner, to educate/onboard, to motivate, to develop, to evaluate, to reward or to discipline, to retain and to celebrate employees.
Each stage is important in an employees’ career cycle but so is HR role in relation to them. A big part of the HR’s responsibility after hiring is to educate the employees about not only their responsibilities and role but also about the company’s policies, the company culture, and ethics regarding discrimination and harassment.
HR communications
Employee communications are one of the most significant elements for the smooth functioning of an organization, increasing organizational productivity and good company culture.
Human resources come into play in employee communication owing to its ability to simplify and improve the relations between employees in the workplace. HR shall work hard to ensure that all the employees adhere to workplace standards, some solely in the workplace others in social media and outside the workplace as well.
Maintenance of open and effective communication is a high priority for a well-functioning HR team. Internal communication allows maintaining positive attitude, morale, and provision of feedback from the ground up to the top levels of the management.
There are various ways and methods which the companies employ to keep the communication channels open. Regular meetings between the supervisors and employees, keeping employees in the loop on the changes in policies, benefits or other regulations, seminars, company activity, and retreats, recognizing good performance, and promoting work-life balance is few of the many ways in which the companies do this.
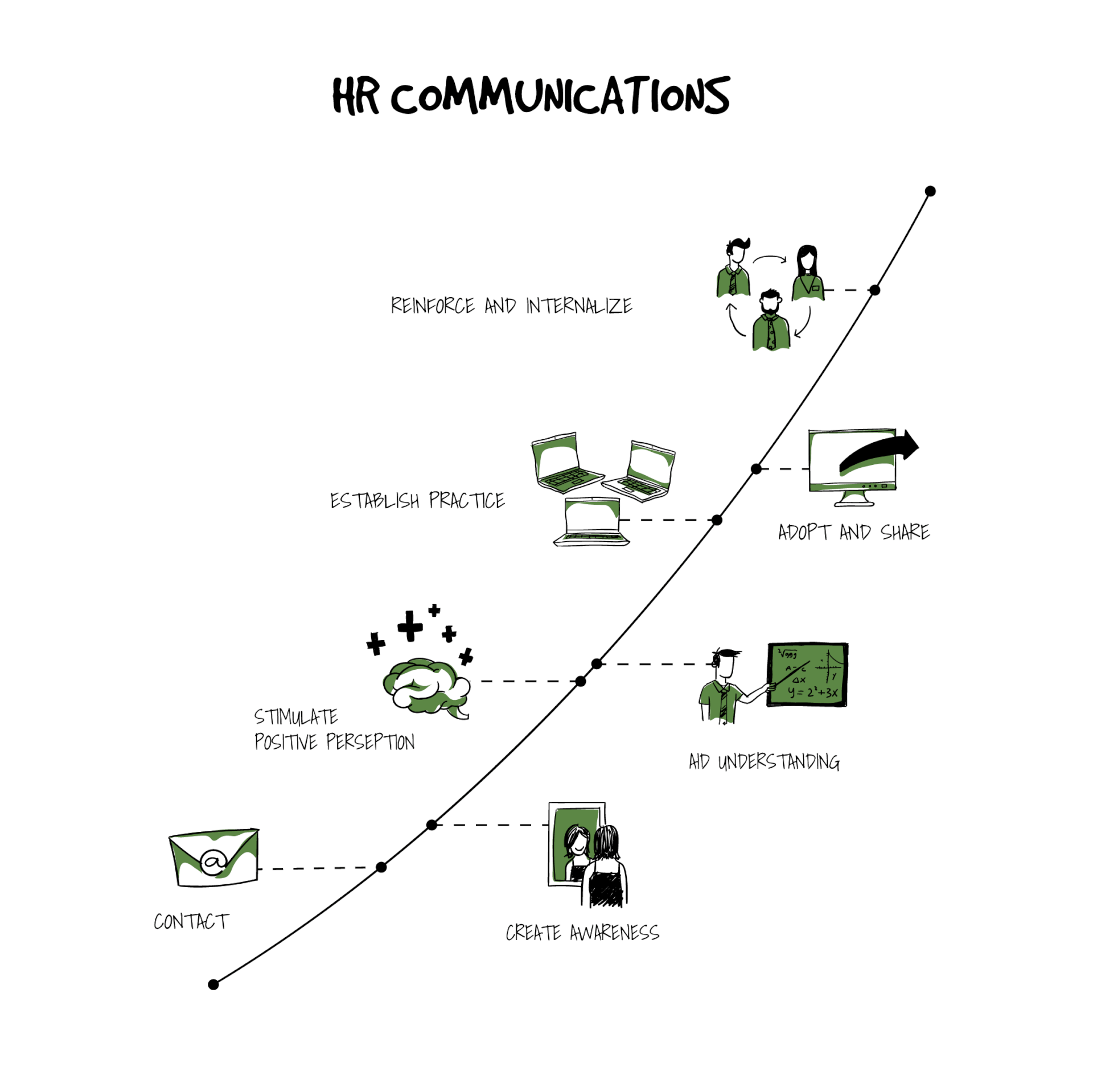
A healthy and strong organization has effective internal communication, including employee self-service applications, as it increases engagement and makes sure that a company’s employees want to work for the company, agree with the vision and perform well for it. It is an ongoing and continuous process that is dynamic.
If there is widespread negativity, low morale, gossip at workplace, an unengaging workforce, bad or subpar performance, and pushback with the conflict between management and employees it could be signs that employee communications have issues.
HR needs to set up strong lines of communication within teams and among employees and managers. An open dialogue in which employees can convey their opinion openly, the management can take their input in making strategic decisions are of top priorities. If employees feel heard and appreciated, it reflects positively across the whole organization. Making a stress-free environment for the employees in which they have flexibility in doing their work will develop strong relations with their team.
The company management or the HR would need to interfere in any situation where the employee feels unsafe or attacked whether by being threatened or assaulted – sexually or racially. At every training seminar or awareness workshop, HR should share notices with all employees about the updated policies and rules of conduct it expects of its employees.
Recruitment and selection
Recruitment and selection process involves the HR’s efforts to effectively screen through the list of candidates to find an individual that fulfills the requirements of the job description and whose skills and vision matches with that of the position the company advertises.
The entire application process, from advertisement to interviewing and to selection, must, as a rule, be open and accessible with no barriers that could discourage someone from applying. When advertised each job description shall focus on skills and abilities required for the position with a language that does not imply that only certain applicants would be considered.
The recruitment must be carried out in assessment against the set-out criteria by the selection panel with a question that relates to the job requirement and that does not oblige to disclose personal information that is irrelevant or offensive with regards to someone’s gender, disability, personal background, race or illness.
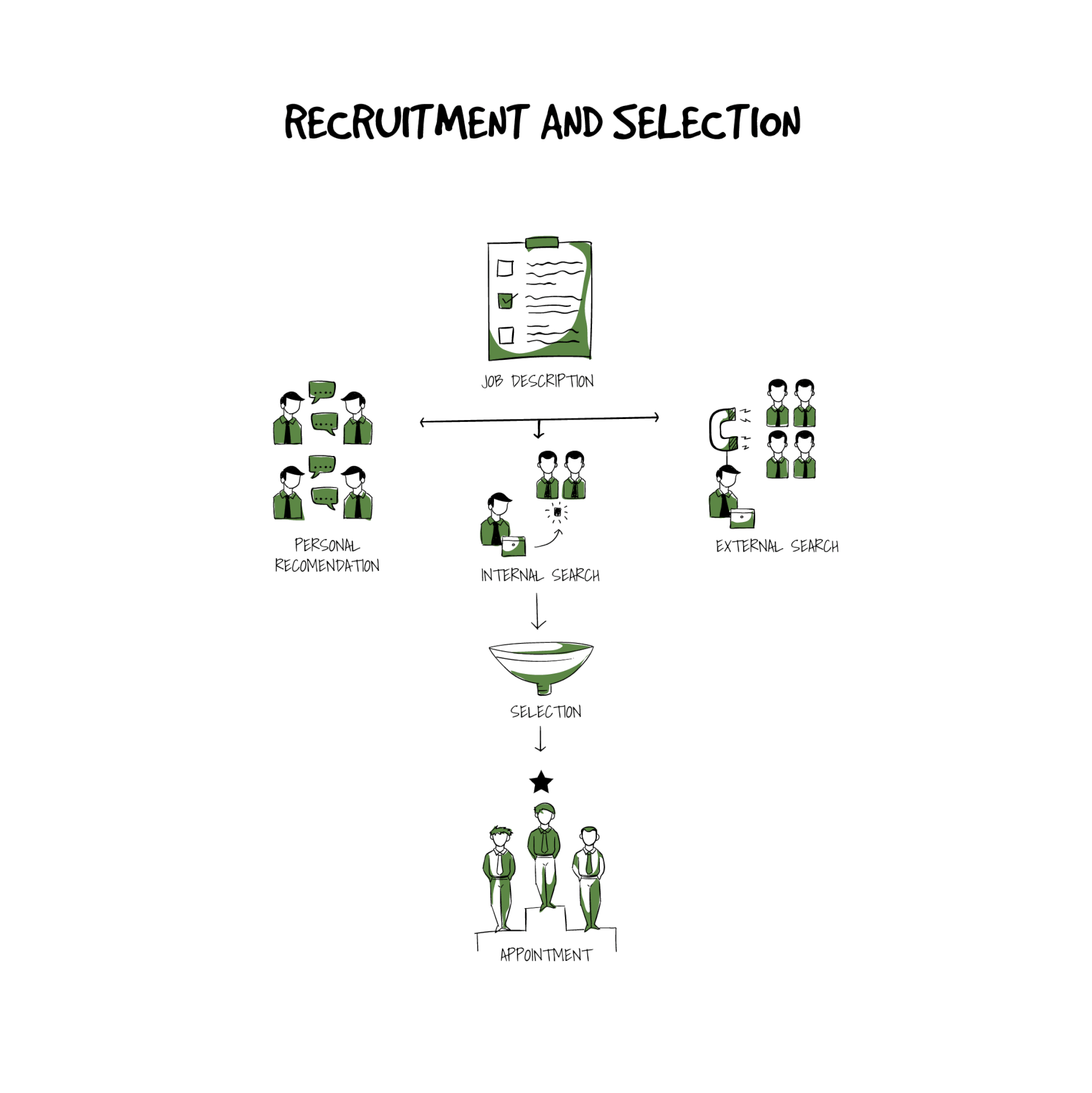
It is the HR’s responsibility that during the entire process, from advertisement to the selection, the applicants and the candidates are treated fairly and within the precepts of all applicable laws. It is imperative that the tests and interviews during the process only assess the ability of the individual to perform the requirements of the job based on the criteria set beforehand.
HR should ensure the privacy of all the applicants and should discuss how the applicant’s information and data would be dealt with beforehand to prevent any violation of confidentiality. It is the employer’s legal obligation to avoid discrimination at every stage of the recruitment process.
Additionally, this stage is ideal for the employers to not only hire the best-suited candidate for the job but also to find someone who matches the long-term vision of the firm. The HR should realize that it is the best time to screen out people who do not agree with the company policies or could potentially be a “negligent hire” that later go on to harass others or cause other damage to the firm.
While the companies should not start out by telling their employees or selected candidates that their personal and professional lives will be under constant surveillance, they could set out the organizational policies and code of conduct all employees should subscribe to.
Evaluating staff
The big part of the HR work and a major concern for employees of any company is performance evaluation. This tool is used to provide feedback and document employee’s performance through a certain period and can clearly communicate job goals.
Performance evaluations are not only an analysis of an employee’s performance based on which they can be rewarded, but it is also a constructive tool which assists in guiding employees on their professional development and improvement. There could be various types of evaluations: annual evaluation covering the calendar year, probationary evaluations for new employees before the end of their probation period, special evaluation which can be done on an ad-hoc basis by the supervisor under guidance or instruction of the HR managers.
Staff evaluations can be amazing constructive tools which provide the HR managers and line managers to clearly review the performance of employees and provide feedback on how to improve or maintain their performance. The results can aid the HR in setting performance standards and goals based on the outcomes of the review.
Evaluations recognize the professional accomplishments of individual employees, the performance of the entire company and improve working relationships. If evaluation provides useful results they can help in setting an employee on the path to a promotion or other reward. Conversely, it can also mean a disciplinary action for an employee who consistently shows no improvement or even degrades.
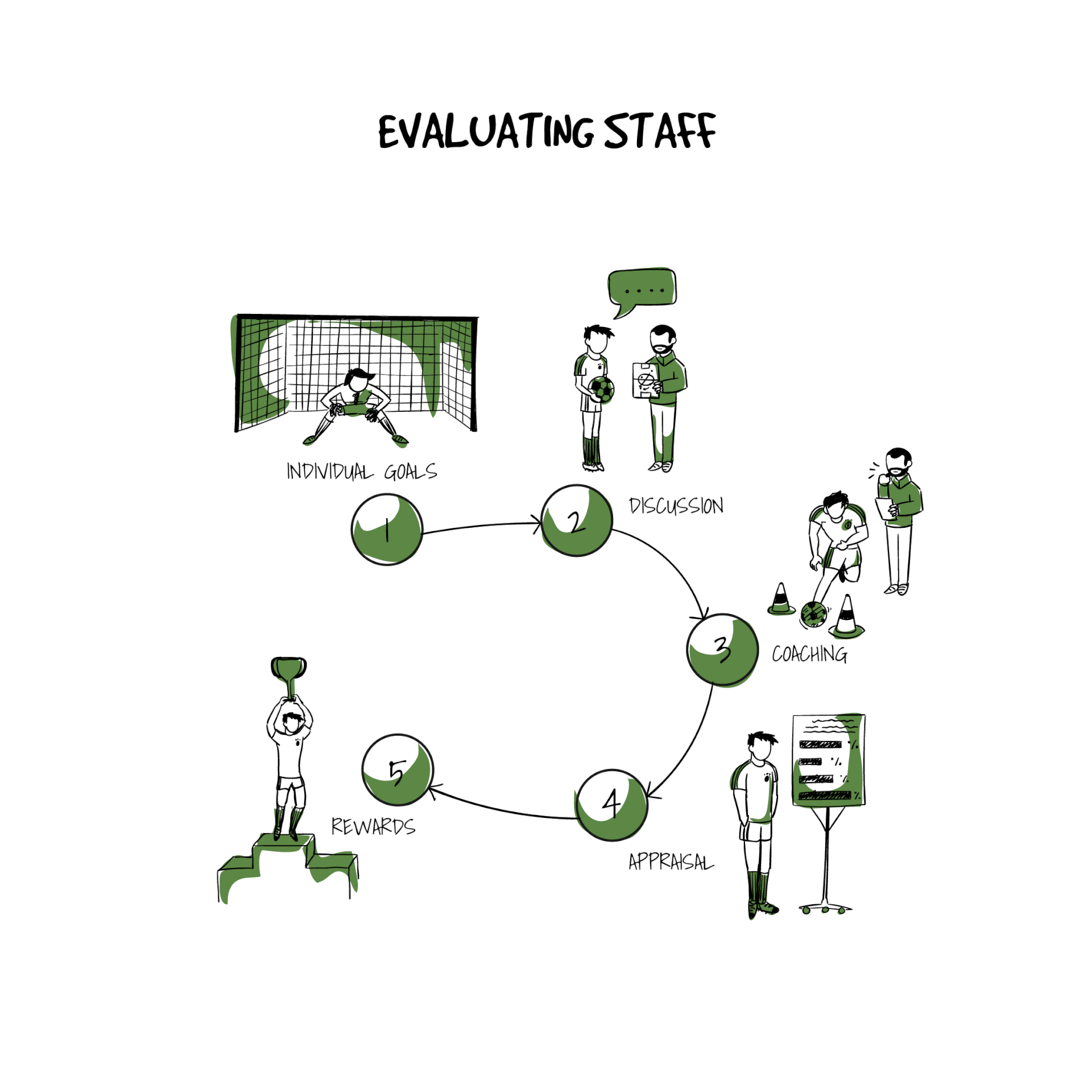
Given this nature of evaluations, they hold great importance. These results can, therefore, help the human resource managers in identifying the employees who do not show performance improvement, nor show positive results for the training and development investment the company has made. Thus, armed with data, analytics, results and communicated information from the direct supervisors, line managers and the employee itself a decision can be made whether the organization would benefit from letting the employee go or if training and development programs need to be redesigned.
Any evaluation process has some basic premise which both the employee and supervisor are aware of. This includes the ability to set and monitor goals, provide and document feedback, review description of the position, employee’s self-evaluation, rating the performance, reviewing goals, summarizing evaluation, acknowledging and appealing the evaluation.
Given the weight the evaluation process holds, it is critical for organizations and HR to ensure a free and fair process that does not put any employee at an unfair advantage or disadvantage. This falls even in the category of workplace relationships, particularly between a supervisor and an employee, which can be seen by employees as a conflict of interest.
Motivation and rewards
A motivated workforce is amongst the strongest assets an organization has that translates into greater success and revenue for it. Motivation and rewards are two positive reinforcement tools that generally have a favorable impact on people’s behavior and performance. Naturally, these tools motivate employees to work towards achieving the organizational goals.
Rewards system by way of motivating the employees induces them to work at a higher level of productivity, making for an efficient and effective workforce that reaches its objectives and goals. In the same way, employee satisfaction, engagement, and contribution will motivate the organization to provide a free, just and equitable evaluation and rewards system.
Rewarding employees fall in the HR’s area of responsibility, a task with heavy implications provided that an unmotivated workforce can disrupt the organization’s efficacy due to lack of focus and undesirable results. Thus, rewards system holds a great magnitude of power in the eye of the managers with the understanding that this system highly influences employee behavior and productivity.
While intrinsic rewards are important in their capacity to create personal satisfaction in an employee due to their efforts being recognized, financial rewards have to follow it up to maximize employee motivation. Tangible rewards like extra vacation days, promotion and financial benefits are important to the majority of employees and create a synergy effect with intrinsic rewards.
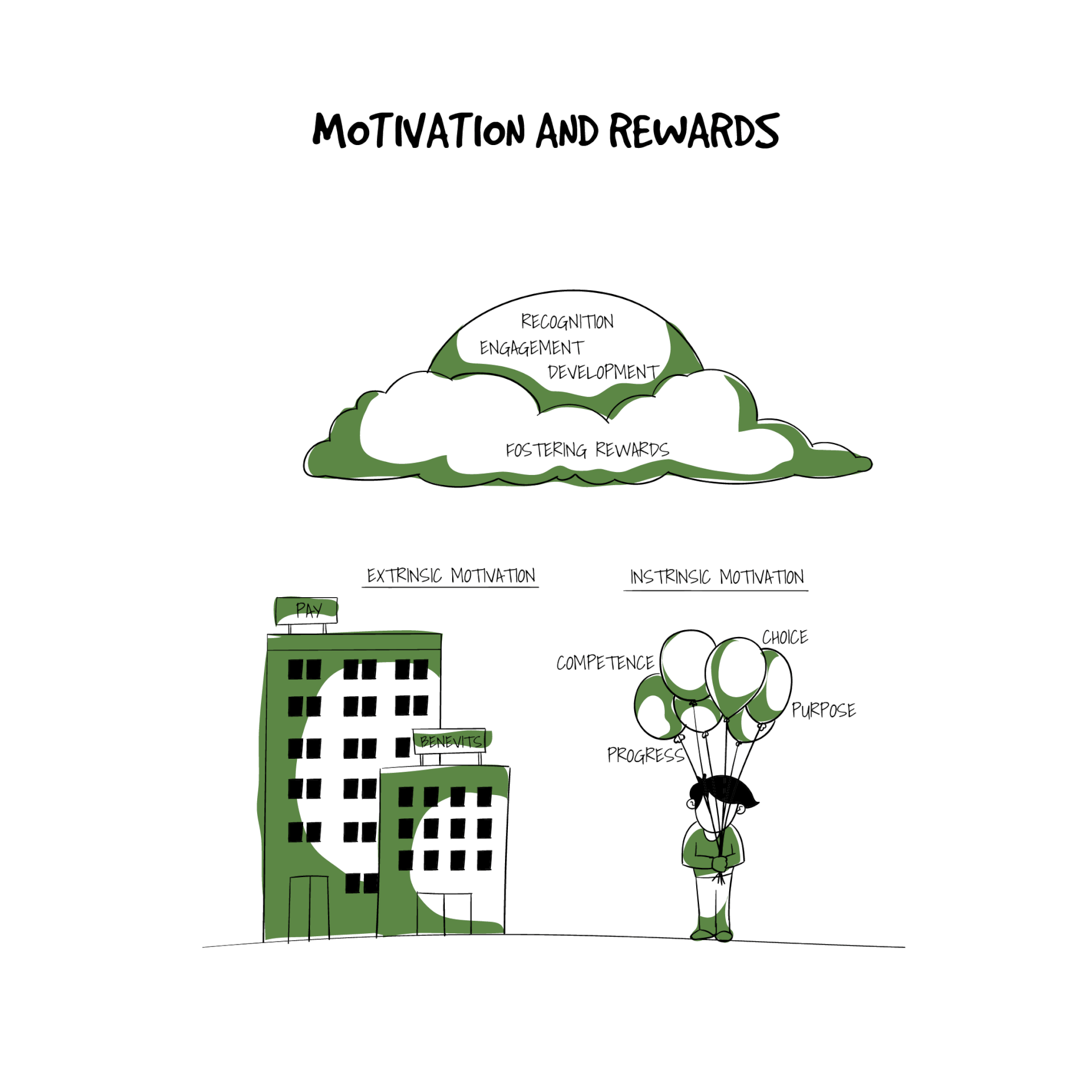
All data points towards the fact that positive rewards like pay raises, celebrations and promotions have a generally positive impact upon employee performance, motivation, commitment and a good company environment. Contrariwise, lack of positive rewards impacts and weakens company commitment, leading to employees raising questions on the fairness of the evaluation and motivations process.
Rewards and motivations should solely be the result of performance evaluation. Gender, race or any other personal characteristics should never come into play when a decision is taken regarding such matters. Employees should also take into account that apart from their performance, their behavior can also negatively impact their ability or probability of being rewarded. That is, if employees do not adhere to the company code of conduct, company ethics, organizational policies, and programs, it will affect their performance review and thereby, their chances of being rewarded.
Financial rewards coupled with intrinsic motivation acts as the perfect cocktail to re-energize workforce. In conjunction, these rewards motivate the workforce to perform better and assist in achieving long-term management goals.
Team building
Employees are one of the most important assets of a company and its biggest investment. This seemingly beaten down tirade on importance of employees though may be seen as all talk if not supported by HR management systems. Building on the importance of employees as team members, while investment in each employees’ professional development is critical.
Team building efforts derive their significance from their ability to build trust, reduce conflict and increase open communication and collaboration. It can also be a great way to address the disengagement employees may feel from their organization. Team building can strengthen the corporate culture and help create efficiency in an organization.
As employees feel united around a common purpose they generate greater productivity. Not only can it provide HR insight into how employees perform together as a team but also help set tasks with company objectives in mind. The workforce can then be engaged together, as a team, thus achieving the objective of not only creating better teams but also benefit the business.
Team building activities can engage employees with each other and help them perform better by communicating better, bouncing off ideas off each other and being more creative and productive. It can also impact the company culture positively by creating a friendly environment which puts the employees at ease and boosts their morale.
Company’s retention rates can also benefit from these team building activities. By ensuring that HR deals with employee conflicts and finds the amicable resolutions it creates higher employee retention.
Millennials that are joining companies nowadays have their work ethic and belief about what a corporate culture should be are very different from previous generations. Their views on workplace relationships, employee privacy, company’s reach over an employees’ life, work-life balance and workplace friendships are quite different.
HR’s mission today in the world of online distractions and dynamic business environment is getting even harder. However, in modern work environment HR professionals strive to design policies and team-building efforts that allow teams to gel more and to feel connected to the company.
Leadership strategy and styles
It is essential that employees see their manager or supervisor manifesting leadership competencies. A focus on competencies and skills development by any executive improves leadership. It should be taken into consideration that any leadership skill required may differ with respect to a particular position.
Given the importance of leadership strategy, HR professionals need to consider some competencies when selecting and developing leaders. Through looking at the individual’s skills and competencies and comparing them to those expected of a leader, HR professionals can map out the development areas and what is further needed for the selected individual’s success in a leadership role. This method can help organizations make better-informed decisions in the process of hiring, developing and promoting leaders.
Cultural sensitivity, open-minded thinking, flexibility in tactics, ability to deal with complex situations, resourcefulness, personal energy, integrity, value-added skills, ability to manage change, risk-taking, innovation, effective communication are some of the qualities that should be reflected in a good leader.
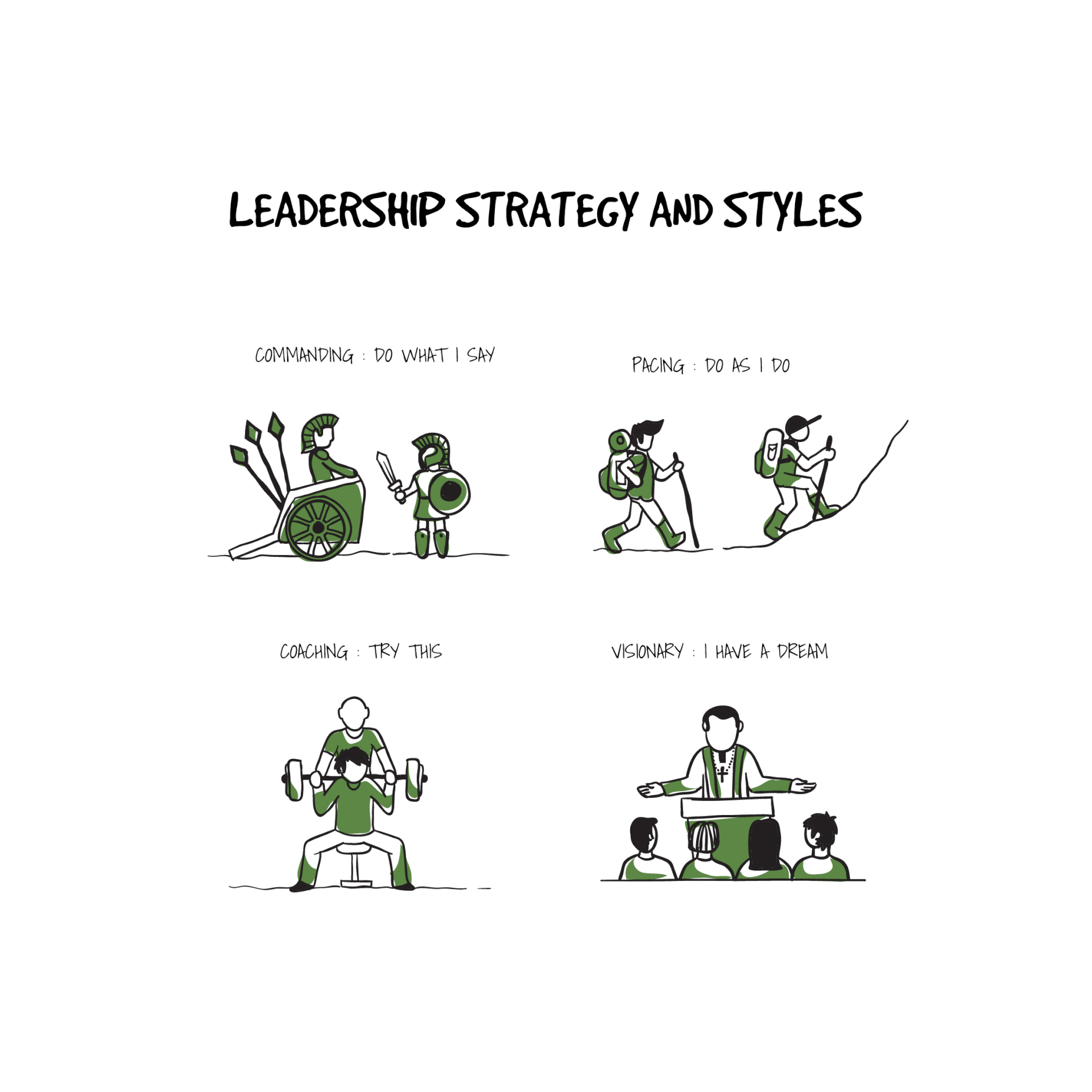
Good leadership with strategy and style has the ability to influence others to make voluntary decisions which enhance the organization’s success in the long term. There is a balance between the analytical, financial and human dimension of a leader.
Whether you are a directive leader, visionary, democratic, collaborative, incubating, transformational, or even a mix of some of these features, being a good leader means to do the right thing for your organizations and for your employees meanwhile also motivating others to do so. It is not only important to be emotionally intelligent, analytically aware, to develop a high performing team but also to distribute leadership.
A leader needs to explore several leadership styles and strategies to engage staff and drive the company towards meeting its goals while also setting new ones. In a competitive and risky environment, a good leadership style has the ability to give the organization an edge by compelling others to go on the needed course.
Business cultures
The business culture of any organization makes it unique and as a symbol of its beliefs, vision, behaviors, and values, a sum of all those things are vitally important from HR management perspective.
A good workplace that is conducive to driving employee engagement, talent acquisition, employee retention, talent development, and high productivity is clearly a marker of a positive culture. It influences and defines the ‘personality’ of an organization and reflects the values and beliefs of its leadership and management.
Company culture has always been important, but the significance attached to it is increasing even more so with the millennials joining the workforce. New employees when deciding on a company and contemplating other offers put weight on how they perceive a particular company’s culture. If you hear that a company has cases of sexual harassment, diversity or privacy issues, any of those things could be a deal-breaker.
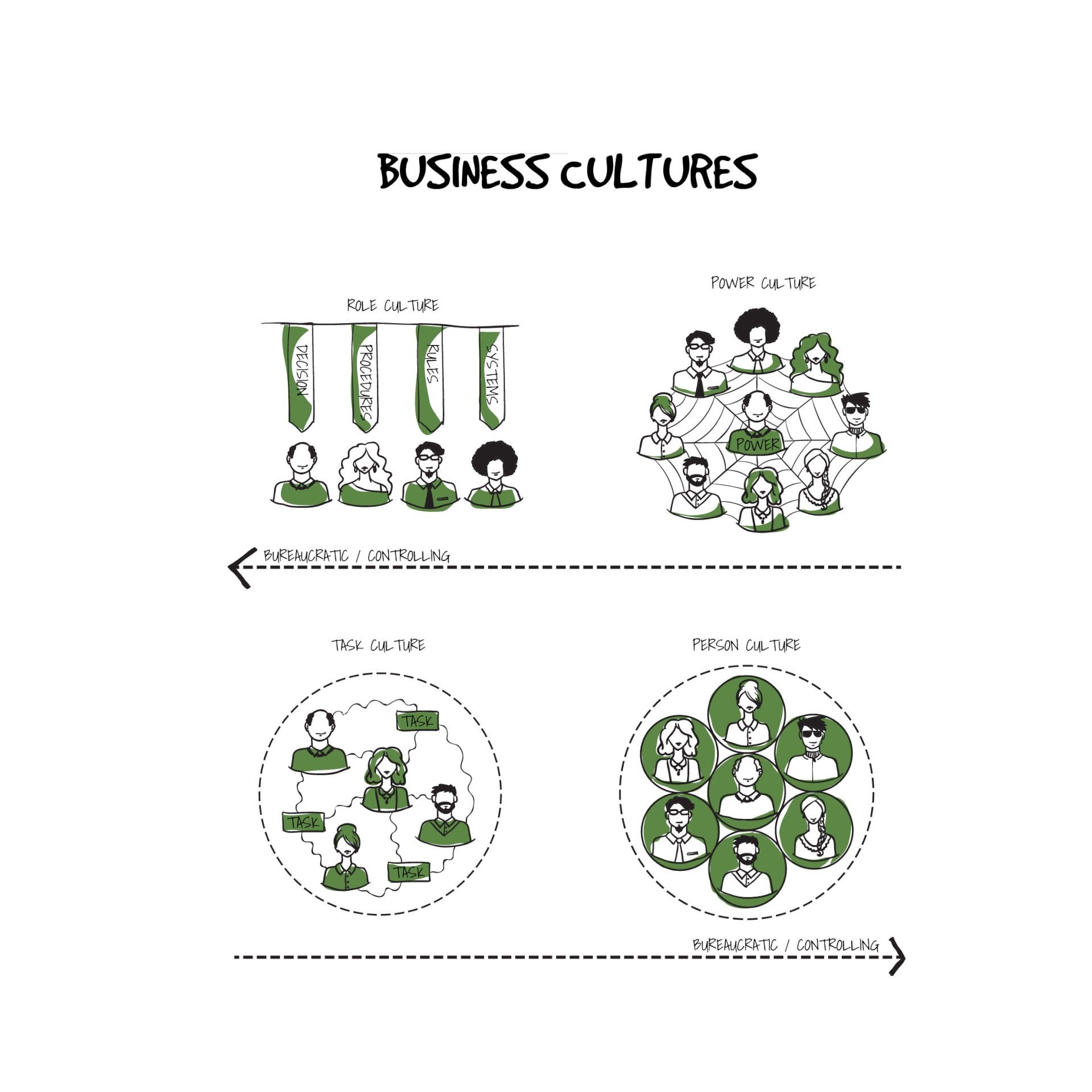
Company culture is set by the organization’s leadership and management. It reflects their values and expectations of what the company stands for, how employees interact and execute their job and communicate with the management. Best industry HR practices like recruitment, selection, onboarding, rewards and benefits, evaluation and development will definitely have a positive impact on the workplace and formation of a company’s business culture.
HR professionals and leadership shall take into account the values all stakeholders, social issues, technology and changing trends in deciding which attitudes and behaviors to promote in their business culture. How employees conduct themselves both inside and outside workplace also need to in compliance to existing laws like EEOC or NLRA.
Company stakeholders
Human resource system is designed to serve an organization’s key stakeholders. A broad, multi-stakeholder partnership on HR issues is the right way in a dynamic, rapidly changing environment. By stakeholders, it is meant that any groups of people who have a significant claim in the operations or in the output of an organization.
It is key to note that few of these stakeholders are the internal members of the organization itself, much like the directors and employees, while others are external, like regulators or local community. Together as a whole, the stakeholders can largely affect the formulation of the business strategy and company policies.
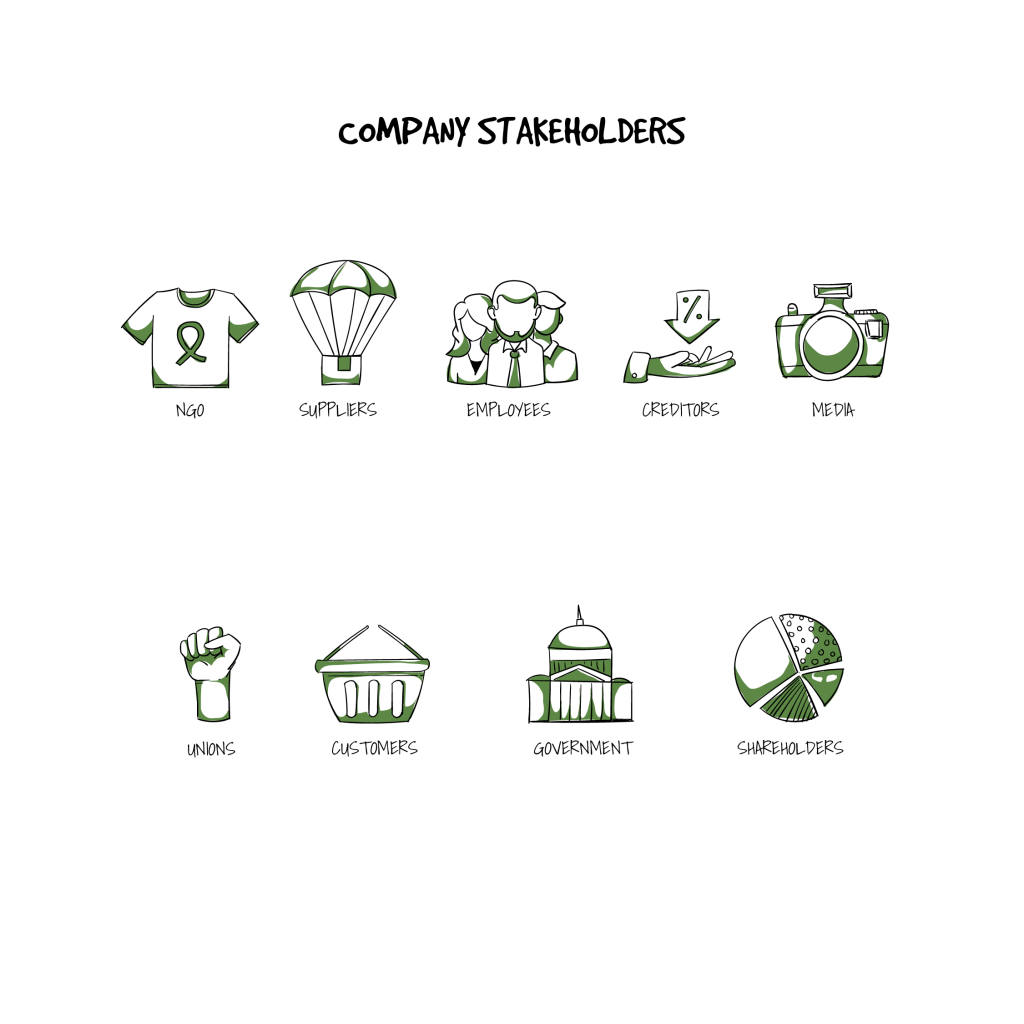
HR professionals have to operate in a complex web of interaction with a diverse system of actors. This interaction with the different group would have resulting management practices as each stakeholder tries to further influence and protect their interests. HR professionals need to keep their sights on and pay attention to the employees, their representatives along with other stakeholders.
If not for this the HR professionals might lose the involvement of one of its most important stakeholders when shaping the employment relations in organizations. Stakeholders’ input on change, spreading information and considering alternatives is significant for creating mechanisms for successful HR management.
Company hierarchy
Like bureaucracies in a government, corporations are also bureaucracies. Some are big, some are small, and some are on a scale much larger and complex than some governments. Each carries its own policies, its own laws, and cultures.
However, all these bureaucracies work the same way. They are divided into different tiers with each tier having a specific position in the whole structure and a functional area of responsibility with their own goals and targets. They also have their own authority and report structure.
These are executives, management and, line workers. This structure – with the management having its own tiers – is organized in a pyramid structure which, true to the shape, means as the structure climbs up a large number of personnel decreases, and responsibility and authority increases. This at the top are the ranks of the upper management.
A well-drafted hierarchy of the organizational workforce makes it possible to evaluate a firm’s strategies, the plans to put in place that will make it possible to reach the goals and to divide the whole workforce into organizational functions. However, despite this division between the responsibilities and authority, for an organization to be successful it needs to have good coordination between all levels of management.
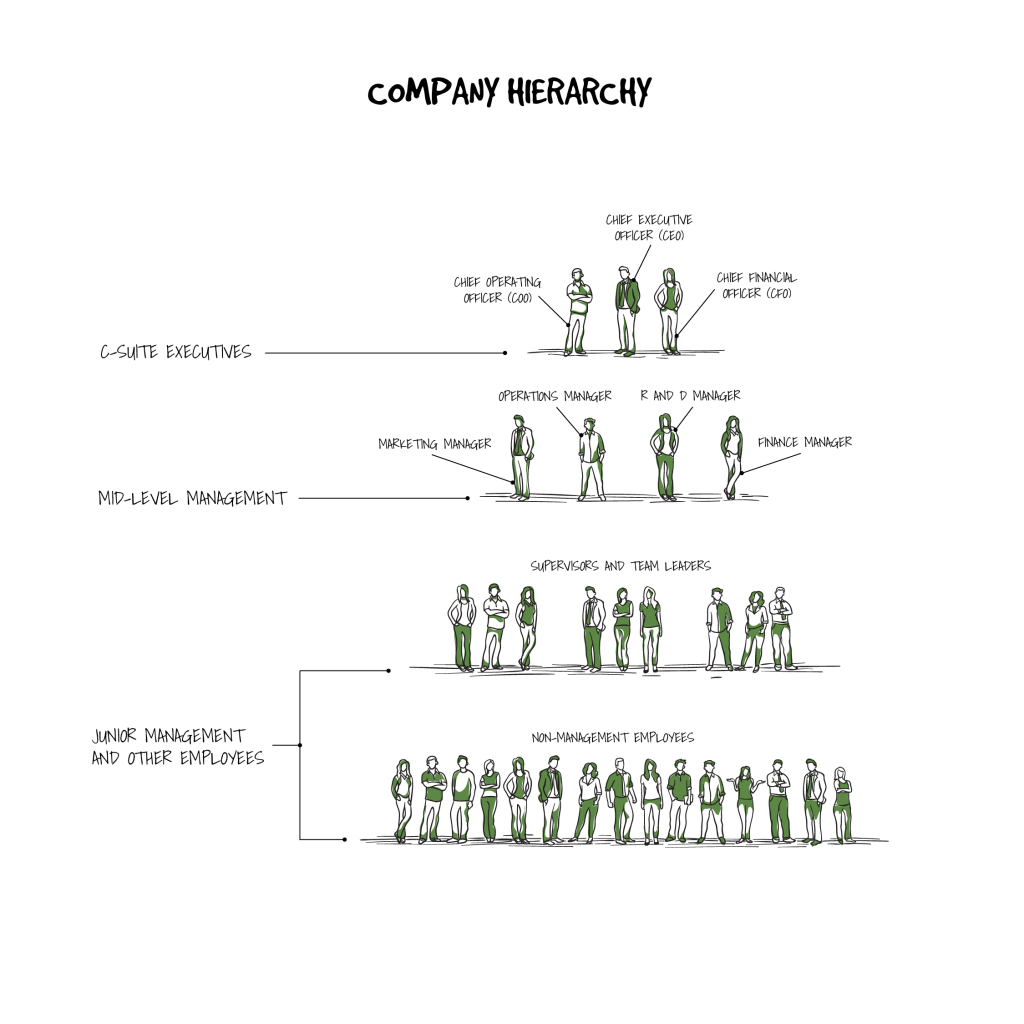
A company hierarchy thus defines various levels of power distribution in its structure. The basic hierarchy is top management, middle management, and a junior management in the descending order.
The first-line management presides over the supervisor, office manager, and team leaders, in the mentioned order. The middle management, on the other hand, oversees the general manager and the regional manager. As far as the top management is concerned, the hierarchy starts with the CEO, the board of directors with the chairman holding the most authority.
Company hierarchy not only oversees the core aspects of management but also coordinates operations of employees and delegates the policies and expectation of the management to the employees. Integrating the functions of all the tiers optimizes organizational performance and borrows heavily from the efforts of the human resource management which aligns personnel with business strategy to produce synergy effect that translates into efficient workforce, better productivity and higher revenues.